
Tenses are fundamental to effective communication, as they allow us to convey when actions occur within the framework of language rules. Among these, the future simple tense plays a vital role in English, helping us articulate intentions, predictions, and events that are yet to happen. We will delve into the structure and application of this future tense by thorough explanations and helpful examples.
Definition: Future simple
The future simple (also: simple future) tense is a verb tense used to describe actions or events that are expected to happen at a time later than right now. It is one of the basic tenses in English, along with present simple and past simple. It is often used to express intentions, predictions, promises, offers, or spontaneous decisions that are made at the moment of speaking. As with the present perfect, an auxiliary verb is needed with this tense.
Formula of future simple active voice
The future simple is formed with the help of the auxiliary verb “will” followed by the base form (or infinitive) of the main verb. The structure is consistent across all subjects and pronouns, making its form quite simple since one doesn’t need to take subject-verb-agreement into account.
Structure
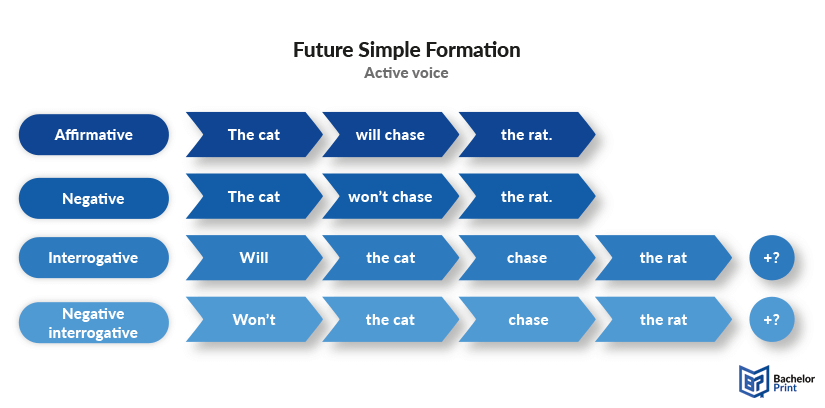
Subject + will + infinitive + rest of the sentence.
With the simple future, contractions can be used, especially in speech. We have provided a table depicting the shortened future simple forms for each pronoun, along with simple future’s one exception and the negative will-form.
| Long version | Contraction |
| I will study. | I'll study. |
| You will study. | You'll study. |
| He will study. | He'll study. |
| She will study. | She'll study. |
| We will study. | We'll study. |
| You will study. | You'll study. |
| They will study. | They'll study. |
| Someone will not study. | Someone won't study. |
Note: “It will” should not be shortened in written English. However, it exists in informal speech.
To further your understanding, there are more examples of future simple in active voice below.
Will or shall
In modern English, the usage of “will” in the future simple tense is preferred to the archaic “shall.” “Shall” is traditionally used with “I” and “we” or in literary or poetic speeches or texts. In British English, “shall” is sometimes used for making offers, suggestions, or asking for advice. However, as with American English, its use is declining due to its formality and can be easily replaced with “should.” Below are numerous examples of the use of “shall” in proper sentences.
Active question form of future simple
To form questions in the future simple tense, we adjust the sentence structure by moving the helper verb “will” to the front of the sentence, while the verb remains in its base form.
Structure
Will + subject + (not +) infinitive + rest of the sentence?
Or
Won’t + subject + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
Questions with question words
For questions with added question words in future simple, just add the fitting question word before “will.”
Negative questions with question words
Since this future tense is called “future simple,” the “simple” stays simple throughout all active forms, as seen in the examples below.
Below, we have created an illustration depicting the structures of the future simple tense in active voice.
Formula of future simple passive voice
Now that we have finished going through the active voice of future simple in the previous paragraphs, we can now delve into the form of its passive voice. It is formed by using “be” and the past participle (3rd past form) of the main verb. Similarly to other tenses, if people are involved in the passive future simple tense, we use the “by” agent to indicate the doer of the action. The object of an active future simple sentence turns into the subject of the passive sentence.
Structure
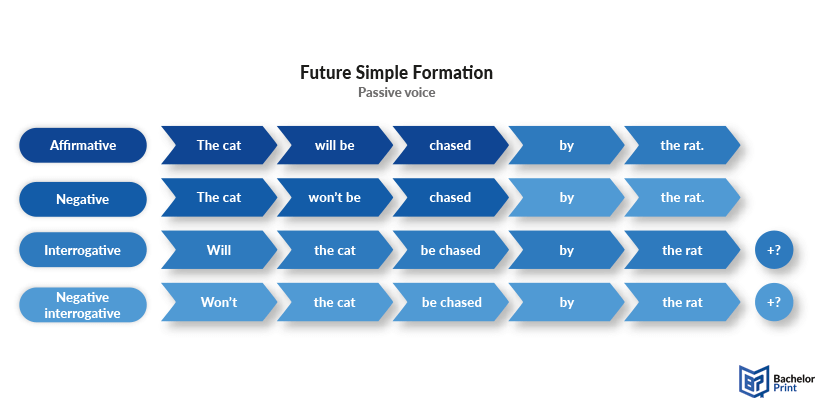
Subject + will be + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Structure
Subject + will (not) be + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Or
Subject + won’t be + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Structure
Will + subject + be + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Structure
Will + subject + not be + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Or
Won’t + subject + be + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
A summary for future simple in passive voice can be found below.
Indicators and usage of future simple
The future simple tense is a fundamental aspect of English grammar that enables speakers to express future actions and predictions with ease. As with other tenses, time expressions make it easier for native English speakers and English learners to identify. Future simple’s situational uses and indicators can be found below.
Predictions
This tense is often used to make predictions based on evidence of opinions.
Spontaneous decisions
Simple future is used for decisions made at the moment of speaking.
Promises or offers
The tense is also used to make promises or offers.
Intentions
While less common, the future simple can be used to express intentions, although the “going to” form is more frequently used for this purpose.
Fixed events
It can be used to discuss events that are planned or scheduled in the future.
Time expressions
Common time expressions that often accompany the future simple tense include:
- Tomorrow
- Next week/month/year
- In the future
- Soon
- Later
- ✓ Free express delivery
- ✓ Individual embossing
- ✓ Selection of high-quality bindings
Short answers in future simple
Short answers in the future simple tense are concise responses that either confirm or deny the occurrence of future action. They consist of a “yes” or “no” answer, followed by the subject and the auxiliary verb “will.”
Active voice
Structure
Affirmative: Yes, + subject + will.
Negative: No, + subject + won’t.
Passive voice
Structure
Affirmative: Yes, + subject + will be.
Negative: No, + subject + won’t be.
“Will” future vs. “going to” future
Another way to indicate that something will happen and end in the future is by using the “going to” future. It is formed by using the following formula:
Structure
Subject + am/is/are + going to + infinitive + rest of the sentence.
Although both “will” and “going to” forms elaborate on the future, there is a distinction that is important to know for academic writing. While the “will” future is used for spontaneous decisions, predictions, promises, and offers, the “going to” future is specifically used for planned actions and predictions based on present evidence or logical deduction.
Both future tenses can be used to predict something or make a guess. This can be anything from a weather forecast to a prophecy.
When talking about a fixed arrangement that definitely won’t be changed, we use “going to” instead of “will,” as this future form emphasizes the decision.
When you are making a decision on the spot, future simple is the way to go.
In informal situations, “going to” can be used to give an order. However, this can sound rude and bossy, so be careful when using it.
When making a request, we use the interrogative future simple form because using “going to” would sound incredibly rude in most cases.
“Going to” implies that an event is about to happen in the near future or has just begun.
Note: Essentially, one can say, if you are extremely certain that something is going to happen, use “going to,” unless it is a request or a spontaneous decision.
Practice exercise
The practice sentences below cover various aspects of the future simple tense, including both active and passive forms, as well as interrogative and negative structures. On the second tab, you will find the correct conjugations of the English verbs. Have fun!
- She _____ the report by tomorrow. (To finish, active)
- The documents _____ by the manager. (To review, passive)
- He _____ the conference next week. (To attend, negative, active)
- The project _____ by the deadline. (To complete, negative, passive)
- _____ you _____ to New York next month? (To travel, interrogative, active)
- _____ the meeting _____ for next Monday? (To schedule, interrogative, passive)
- They _____ the new product in January. (To launch, active)
- We _____ the renovation this year. (To start, negative, active)
- _____ she _____ you later today? (To call, interrogative, active)
- The presentation _____ by tomorrow. (To prepare, negative, passive)
- She will finish the report by tomorrow. (To finish, active)
- The documents will be reviewed by the manager. (To review, passive)
- He won’t attend the conference next week. (To attend, negative, active)
- The project won’t be completed by the deadline. (To complete, negative, passive)
- Will you travel to New York next month? (To travel, interrogative, active)
- Will the meeting be scheduled for next Monday? (To schedule, interrogative, passive)
- They will launch the new product in January. (To launch, active)
- We won’t start the renovation this year. (To start, negative, active)
- Will she call you later today? (To call, interrogative, active)
- The presentation won’t be prepared by tomorrow. (To prepare, negative, passive)
FAQs
The future simple is a tense form that describes actions or events that will occur in the future. It is used to express predictions, spontaneous decisions, promises, offers, and intentions related to future events.
An example for future simple is the following sentence:
- She will visit her grandma next weekend.
- He will start a new job next month.
- They will travel to Paris this summer.
- I will call you later tonight.
- She will finish the project by tomorrow.
- We will have a meeting on Friday.
- The movie will begin at 8 PM.
- You will receive your package soon.
- They will announce the winner tomorrow.
- He will buy a new car next year.
- The company will launch a new product next quarter.
You should use the future simple tense when you want to:
- Make predictions
- Express spontaneous decisions
- Make promises or offers
- State intentions
- Describe fixed events
