Understanding independent vs. dependent variables of experimental design, statistical modelling, and hypothesis testing in various disciplines shapes a bedrock of methodology. An independent variable is the factor manipulated to observe its effect, whereas a dependent variable is the outcome or response that is measured. In essence, the independent variable causes a change, and the dependent variable is what is being affected. Distinguishing between independent and dependent variables is vital for organising experiments, interpreting results, and drawing meaningful conclusions. Learn more in this article.
Definition: Independent vs. dependent variables
To distinguish independent vs. dependent variables, it is simplest to define each type of variable individually:
- An independent variable is a value independent of other variables in scientific research. It is what the researcher changes to trigger an effect on other variables.
- A dependent variable is a value influenced by changes in the independent variable. Therefore, the difference between independent vs. dependent variables is that the former is the cause while the latter is the effect.
- ✓ Free express delivery
- ✓ Individual embossing
- ✓ Selection of high-quality bindings
Independent vs. dependent variables in research
Independent and dependent variables are applied in experimental and quasi-experimental research. Check out the following examples of research questions and their corresponding independent vs. dependent variables:
| Research question | Independent variable | Dependent variable |
| Do plants grow faster in natural or artificial research? | The type of light the plant grows under | The plant’s growth rate |
| What is the impact of dieting on mental wellness? | The participation or lack of participation in dieting | The mental wellness rate |
| Is CBD effective for migraine pain reduction? | The presence or absence of CBD use | The frequency and intensity of migraines |
| To what extent does the work environment affect productivity? | The type of work environment | Productivity rates |
In experimental research, you analyse the results by visualizing your findings or using descriptive statistics. T-tests and ANOVAs are perfect for analysing data and answering research questions. There are different types of independent vs. dependent variables in research. The following will delve into the various types of independent vs. dependent variables.
Types of independent variables
There are two key types of independent variables:
- Experimental independent variables
- Subject variables
Experimental variables
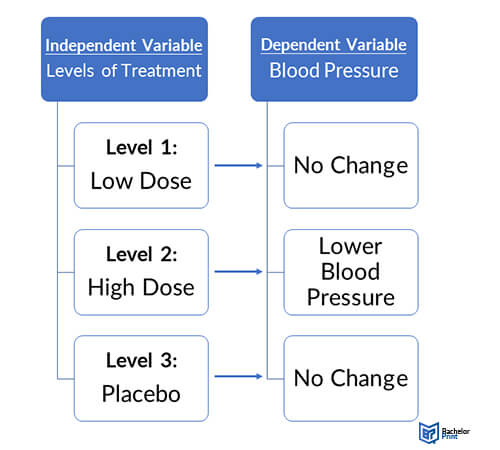
Researchers manipulate independent variables in experiments to evaluate and observe how they impact the dependent variables. For instance, you can apply only two levels to determine if the independent variable impacts the dependent variable.
Subject variables
Subject variables are the values or qualities that vary across subjects that the researcher cannot manipulate, like age, gender, ethnicity, and race. A researcher cannot randomly assign subject variables to participants. Instead, you must create an experimental design where you can compare the outcomes of subject groups with specific characteristics. Subject variables are applicable in quasi-experimental designs with no random variable assignments. Unfortunately, non-random assignment risks research biases like sampling and selection bias.
Dependent variables
A distinction between independent vs. dependent variables is that dependent variables are the changes that occur from manipulations of the independent variable. The records that researchers note after manipulating an independent variable are the dependent variable.
Detecting independent vs. dependent variables
Identifying independent vs. dependent variables in an academic or complex research paper can be difficult because independent vs. dependent variables vary from one study to another. Below are guidelines for distinguishing independent vs. dependent variables.
Identifying independent variables
Ask yourself the questions below.
- Is the researcher manipulating or controlling the variable as a subject for grouping the subjects in the study?
- Does the variable precede the other variable (in time)?
- Is the researcher attempting to study if or how the variable affects another variable?
Identifying dependent variables
Ask the following questions.
- Is the variable measured as the research outcome?
- Does the variable rely on another variable in the experiment?
- Does the researcher measure the variable after altering another variable?
Illustrating independent vs. dependent variables
Another important thing to learn is illustrating independent vs. dependent variables. You can use charts or graphs to illustrate independent vs. dependent variables in quantitative research.
The dependent variables usually go on the x-axis, whereas the independent variables are on the y-axis. The independent vs. dependent variables illustration type will depend on your formulated research question.
- Bar charts are perfect for categorical independent variables
- Line or scatter pot graphs are perfect where both your variables are quantitative
Example
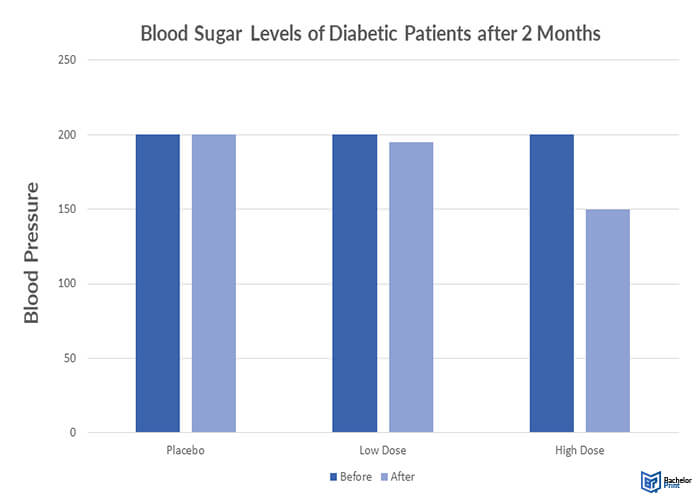
You collect data on the blood sugar levels of diabetic patients before and after a novel treatment over a specific period. Place the independent variable, the treatment level, on the x-axis, and the dependent variable, the blood sugar level, on the y-axis.
Plot bars for each treatment group before and after the treatment to illustrate the blood sugar difference. It will show a slight difference in blood sugar levels in the placebo and low-dose subject groups and substantial improvements in the high-dose group.
FAQs
The difference between independent vs. dependent variables is that independent variables are manipulated in research, while the dependent variables are affected by the changes in other variables.
No, there is a difference in independent vs. dependent variables. So, a value can be dependent or independent, but not both.
Yes, despite the independent vs. dependent variables distinctions, you can use more than one of each in a complex study with multiple research questions.
The key difference between independent vs. dependent variables is that independent variables are the cause, while dependent variables are the effect.
