
Participles, often hailed as the chameleons of language, hold a unique position in the realm of grammar, seamlessly blending the dynamism of verbs with the descriptive prowess of adjectives and adverbs. In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to unravel the multifaceted nature of participles, exploring their formation, usage, and transformative impact on the fabric of language rules.
Definition: Participles
Participles are verbal forms that are derived from verbs and can function as adjectives or adverbs in a sentence structure. They retain some characteristics of verbs, while also taking on qualities of adjectives or adverbs. Basic participles are used to provide additional information about nouns or modify verbs, adding detail, description, or clarification to sentences.
They are related to verb conjugation because they are forms of verbs, but they are considered non-finite verb forms. Unlike finite verb forms, those non-finite forms do not show tense, mood, or person, and they cannot function as the main verb in a sentence on their own. However, participles are still important in verb conjugation because they are used alongside auxiliary verbs to create various tenses, aspects, and voices.
Types of participles
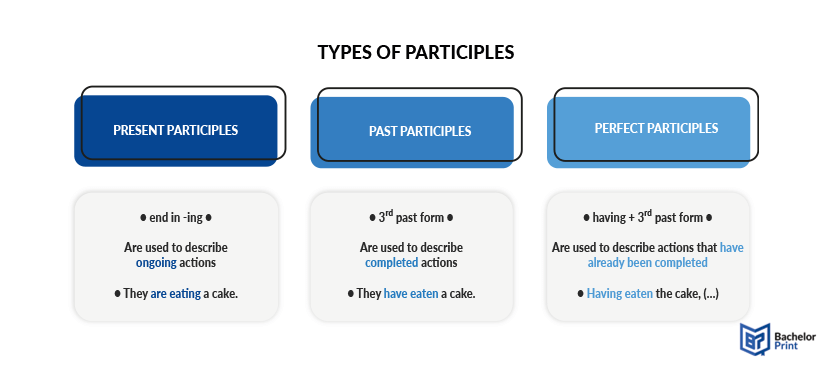
There are typically three types of participles in English: present participle, past participle, and perfect participle. Each one will be explained in this paragraph, together with examples.
Used to describe ongoing or simultaneous actions or states.
The present participle is usually formed by adding -ing to the base form (infinitive) of the verb.
They can be used in four ways:
- in continuous (progressive) tenses, using “am/is/are,” “was/were,” or “will be” e.g.
- as a gerund, where the verb acts as a noun
- as an adjective that modifies a noun
- as part of a participle phrase, adding more information
The following examples are in the same order as in the box above.
However, there are some special rules for irregular verbs regarding the ending of English present participles in some cases.
- Verbs ending in a silent -e → no e + ing
- Verbs ending in -ee or -oe → + ing
- Verbs ending in -ie → y + ing
- Verbs ending in -c → ck + ing
- Verbs with one consonant and short vowel.
The table below illustrates examples of special cases.
Used to describe completed actions or states.
The past participle of regular verbs is formed by adding -ed or -d to the infinitive of the verb.
The past participle of irregular verbs is formed by adding -t, -en, or other irregular endings to the infinitive of the verb.
They can be used in four ways:
- as part of a perfect tense, using “have,” “has,” “had,” or “having” e.g.
- in passive voice constructions
- as an adjective
- as part of a participial phrase, adding more information
The following examples are in the same order as in the box above.
There are, however, special rules for verbs that are irregular in the past participle.
- Verbs with the same infinitive, past simple, and past participle.
- Verbs with only the same past simple and past participle.
- Verbs with only the same infinitive and past participle.
Used to describe actions that have already been completed.
Perfect participles are formed by combining the auxiliary verb “having” with the past participle verb form.
Perfect & continuous tenses
Participles play a crucial role in forming perfect verb tenses in English. Perfect tenses indicate actions that are completed at a certain point in time, or before another action. Participles are combined with auxiliary verbs to create these tenses.
Participle are also important in continuous sentences. In English grammar, the continuous tenses indicate actions that are, were, or will be happening at a specific moment, or before another action.
| Present perfect (has/have + 3rd form) |
Past perfect (had + 3rd form) |
Future perfect (will have + 3rd form) |
| She has studied Spanish. | She had studied Spanish. | She will have studied Spanish. |
| They have eaten breakfast. | They had eaten breakfast. | They will have eaten breakfast. |
| Present continuous (am/is/are + -ing) |
Past continuous (was/were + -ing) |
Future continuous (will be + -ing) |
| She is studying Spanish. | She was studying Spanish. | She will be studying Spanish. |
| They are eating breakfast. | They were eating breakfast. | They will be eating breakfast. |
Participle phrase
A participle phrase (or participial phrase) is a group of words that includes a participle along with any accompanying modifiers, objects, or complements. A participial phrase functions as an adjective or an adverb in a sentence, providing additional information about nouns, pronouns, or verbs. When functioning as an adverb, it’s sometimes called an adverbial participle phrase, modifying the main verb by indicating time or manner.
When a participial phrase begins a sentence, a comma should be placed after the phrase. If it’s in the middle, it needs to be set off with commas if the information is not essential to the rest of the sentence. Below, you’ll find some examples that will be elaborated on.
- In this sentence, “holding a balloon” is not only a participial phrase, but also a prepositional phrase, acting as an adjective. It modifies the noun “girl” with the intention of providing additional information about her.
- Here, “smiling” is the present participle, and the participle phrase “smiling at everyone she met” modifies the main verb “walked,” so it functions as an adverb. It provides additional information about the way she walked.
- In this sentence, the participle phrase “written by a renowned author” acts as an adjective, modifying the noun “book,” thereby offering additional information about its origin.
- Here, “admiring the architecture” is a participle phrase acting as an adverbial modifier modifying the verb “drove.” The participle phrase provides additional information about how he drove through the city.
Participles vs. infinitives
Both are non-finite verb forms, but they have different functions and uses in an English sentence. Participles act as adjectives or adverbs, while infinitives can function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs.
Participles
- Form: Participles are formed from verbs and typically end in “-ing” (present participle) or “-ed,” “-en,” “-d,” “-t,” or irregularly (past participle).
- Function: Participles function as adjectives or adverbs in a sentence. They modify nouns or pronouns or provide additional information about actions or states.
- Usage: Participles function as adjectives or adverbs in a sentence. They modify nouns or pronouns or provide additional information about actions or states.
Infinitives
- Form: Infinitives are the base form, which is also called infinitive, of a verb which is preceded by the word “to” (e.g., “to run,” “to eat”).
- Function: Infinitives can function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in a sentence. They can serve as the subject or object of a sentence, modify nouns or adjectives, or provide additional information about actions or states.
- Usage: Infinitives are used after certain verbs (e.g., “want,” “need,” “hope”) or as the subject or object of a sentence (e.g., “To travel is her dream,” “She wants to travel”). They can also be used after adjectives (e.g., “It’s important to study”) and nouns (e.g., “The decision to leave was difficult”).
numerous advantages for Canadian students:
- ✓ 3D live preview of your configuration
- ✓ Free express delivery for every order
- ✓ High-quality bindings with individual embossing

Common mistakes
Understanding how to correctly use participles is essential for clear and effective communication. However, common mistakes with participles can arise, leading to ambiguity, confusion, or grammatical inaccuracies. In this paragraph, we will explore some of the most frequent errors encountered when working with participles and provide guidance on how to avoid them.
The grammatical term “dangling participle,” also called a dangling modifier, is an adjective that modifies the false noun. Failing to ensure that the participial phrase logically aligns with the subject of the main clause, often results in dangling participles, which can create confusion.
It’s essential to ensure that participial phrases are used appropriately and effectively to enhance rather than detract from the clarity of the sentence, especially in academic writing.
Some irregular verbs have present or past participles that do not follow the typical additional –ing or -ed pattern. This form of verb can create an obstacle when writing. Below, you’ll find some examples of errors, as well as two lists of irregular words for both present participles and past participles, which can potentially cause problems.
Consistency in verb tense is crucial for clear and coherent writing. Failing to ensure that the tense of the participle matches the tense of the main verb in the sentence, or omitting the auxiliary verb, can be a crucial mistake in your writing.
FAQs
- The running water sounded soothing.
- The singing bird greeted the morning.
- The vase, broken beyond repair, was discarded.
- The movie, seen by millions, was a box office hit.
The three participles in English are present participle, past participle, and perfect participle.
The verb form acts as an adjective or adverb. They usually end in -ing, -ed, or a different form, depending on their past participle. They’re often used in combination with a form of “to be” or “to have.” Look for entire phrases that indicate ongoing or completed actions, or modifiers that provide additional information about nouns or pronouns.
The present participle is formed by adding the suffix -ing to the base form of the verb. The past participle is formed by using the 3rd past form of the verb. The perfect participle is used by using having + the 3rd form of the verb.
