
When we delve into the world of tenses, we step into the realm of time, where language rules and structures guide us in navigating past, present, and future events. Among these tenses, the past continuous acts as a bridge between what was and what was ongoing. In this article, we’ll explore this tense’s grammatical structure along with numerous examples and exercises.
Definition: Past continuous
The past continuous tense, also known as the past progressive, is a verb tense used to describe actions and situations that were in progress at a specific time frame in the past. It is formed by using auxiliary verbs and participles and gives us a way to discuss the background of past events and continuous actions, adding depth and context to descriptions of situations. Unlike past simple, past continuous typically conveys a sense of something ongoing that was either disrupted or that two events were happening simultaneously. Below, you can find three example sentences using the past continuous form.
Formula of past continuous active voice
The past continuous tense in the active voice is formed by combining the past tense of “to be” with the present participle (the “-ing” form) of the main verb. Subject-verb agreement is vital when forming this tense, as it utilizes “was/were” depending on the specific subject or pronoun.
Structure
Subject + was/were + present participle + rest of the sentence.
Active question form of past continuous
To form a question in the past continuous tense, you adjust the sentence structure by inverting the subject and the auxiliary verb. As with the present continuous, the verb form remains the same in the active question.
Structure
Was/Were + subject + present participle + rest of the sentence?
Questions with question words
When forming questions with question words in the past continuous tense, the question word is placed at the beginning, followed by “was/were,” the subject, and then the present participle of the verb.
Negative question form of past continuous
Similarly to other tenses, such as the present perfect, contractions, or inversion of the subject of an active sentence and adding “not” before the verb, can be used when forming negative questions in the past continuous.
Structure
Was/Were + subject + not + present participle + rest of the sentence?
Or
Wasn’t/Weren’t + subject + present participle + rest of the sentence?
Negative questions with question words
Negative questions with question words in the past continuous follow a similar structure, with the question word at the beginning.
The image below depicts all structures of the past continuous tense in active voice.

Practice worksheet
Before we get into the formulas for the past continuous passive voice, let’s solve a quick practice test. The answers for this test can be found in the second tab.
- She ____ a letter when the doorbell rang. (To write, affirmative)
- They ____ dinner when the lights went out. (To eat, affirmative)
- ____ he ____ the guitar all evening? (To play, negative interrogative)
- We ____ the house when the guests arrived. (To clean, affirmative)
- I ____ a novel during the flight. (To read, negative)
- You ____ on your project all night. (To work, affirmative)
- ____ the children ____ in the garden at noon? (To play, negative interrogative)
- She ____ a delicious meal when I called. (To cook, affirmative)
- ____ they ____ the plan when the manager entered the room? (To discuss, affirmative, interrogative)
- I ____ home when it started to rain. (To drive, affirmative)
- She was writing a letter when the doorbell rang. (To write, affirmative)
- They were eating dinner when the lights went out. (To eat, affirmative)
- Wasn’t he playing the guitar all evening? (To play, negative interrogative)
- We were cleaning the house when the guests arrived. (To clean, affirmative)
- I wasn’t reading a novel during the flight. (To read, negative)
- You were working on your project all night. (To work, affirmative)
- Weren’t the children playing in the garden at noon? (To play, negative interrogative)
- She was cooking a delicious meal when I called. (To cook, affirmative)
- Were they discussing the plan when the manager entered the room? (To discuss, interrogative)
- I was driving home when it started to rain. (To drive, affirmative)
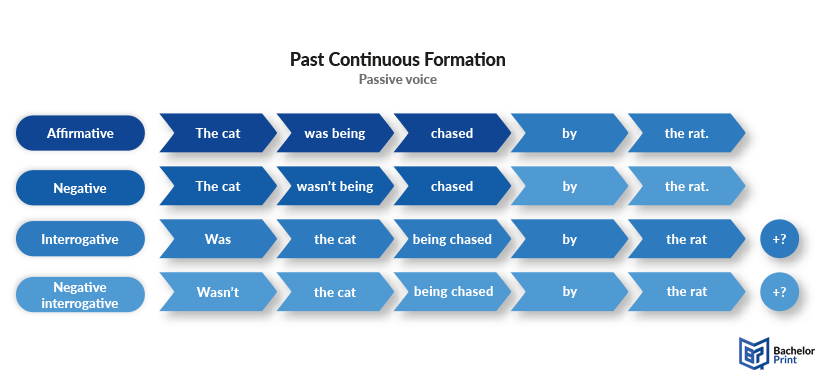
Formula of past continuous passive voice
In the passive voice, the focus shifts from the doer of the action to the action itself or the receiver of the action. The structure uses an appropriate form of “was/were being” with the past participle (3rd past form) of the main verb. The “by” agent is used before the object to indicate the doer of the action.
Structure
Subject + was/were + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Structure
Subject + was/were + not being + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Or
Subject + wasn’t/weren’t + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Structure
Was/Were + subject + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Structure
Was/Were + subject + not being + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Or
Wasn’t/Weren’t + subject + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
The illustration below indicates all passive structures for the past continuous tense.
Indicators and usage of past continuous
Besides a general ongoing action, the past progressive can also be used in other situations. In this paragraph, we will elaborate on its usage and key indicators, along with examples that demonstrate the range of this tense.
Past continuous is often used to describe an action that was in progress when it was interrupted by another action, which is usually in the past simple tense. This usage can be quite complex, as it features subordinating conjunctions, such as once, while, before, etc.
In English, the past continuous tense can also indicate an action that was happening at a particular time frame in the past. This past tense is typically used in criminology, particularly in criminal investigation, when establishing time frames.
The past continuous tense is used with two parallel actions in the past.
Past continuous can also be used with verbs that indicate change or growth.
The past continuous helps set the scene or describe the atmosphere at a particular moment, and is often used in storytelling.
As with the present continuous, the past continuous tense can express habitual actions, typically with a sense of irritation. This occurs by using adverbs such as “always” or “constantly.”
Time expressions
Common time expressions used with the past continuous include:
- While
- When
- At (time)
- All day/night
- As
numerous advantages for Canadian students:
- ✓ 3D live preview of your configuration
- ✓ Free express delivery for every order
- ✓ High-quality bindings with individual embossing

While vs. when
Both “while” and “when” are used as coordinating conjunctions to describe past actions, but there are subtle differences, as they are used differently with the past continuous and past simple tense.
While
Typically used with the past continuous to indicate that one action was in progress when another occurred, or that two actions were happening simultaneously. This tense uses continuous verbs, as not all types of verbs can be used for the past continuous.
When
“When” is often used with the past simple to indicate that one shorter action happened, causing an interruption or marking a specific point in time. This tense regularly features stative verbs (or non-continuous verbs), that describe a state instead of an action.
Short answers in the past continuous
Short answers are commonly used to respond quickly to yes/no questions without repeating the entire sentences. The structure of the short answers reflects the subject and whether the answer is of an affirmative or negative nature.
Active voice
Structure
Affirmative: Yes, + subject + was/were.
Negative: No, subject + was/were not.
Passive voice
Structure
Affirmative: Yes, subject + was/were.
Negative: No, subject + was/were not.
Past continuous vs. past perfect continuous
Past perfect continuous is used to describe an action that had been ongoing before another action. The major difference between these two tenses is that with the past continuous (orange), the action or event continues after the interruption, while with the past perfect continuous (purple), the action stops.
Practice exercise
Here are 10 final practice sentences in both active and passive voice, covering interrogative, negative, and affirmative forms. Answers can be found in the second tab. Have fun!
- ____ they ____ football yesterday afternoon? (To play, interrogative)
- She ____ the book when I arrived. (To read, negative)
- They ____ the new project all morning. (To discuss, affirmative)
- ____ the document ____ by the manager? (To review, passive, interrogative)
- The car ____ by Martina. (To wash, passive)
- We ____ TV when you called. (To watch, negative)
- The report____ by the assistant. (To type, passive, negative)
- ____ he ____ the car when the accident happened? (To drive, interrogative)
- ____ the files ____ by the team? (To organize, passive, interrogative)
- The article ____ by her. (To write, passive, negative)
- Were they playing football yesterday afternoon? (To play, interrogative)
- She wasn’t reading the book when I arrived. (To read, negative)
- They were discussing the new project all morning. (To discuss, affirmative)
- Was the document being reviewed by the manager? (To review, passive, interrogative)
- The car was being washed by Martina. (To wash, passive)
- We weren’t watching TV when you called. (To watch, negative)
- The report wasn’t being typed by the assistant. (To type, passive, negative)
- Was he driving the car when the accident happened? (To drive, interrogative)
- Were the files being organized by the team? (To organize, passive, interrogative)
- The article wasn’t being written by her. (To write, passive, negative)
FAQs
The past continuous tense is used to describe actions that were ongoing in the past until there was an interruption in time.
- Affirmative form: Subject + was/were + verb (-ing)
- Negative form: Subject + was/were + not + verb (-ing)
- Interrogative form: Was/Were + subject + verb (-ing)?
- She was writing her journal when the phone rang.
- They were playing soccer in the garden.
- I was cooking dinner while he was cutting the vegetables.
- The students were studying for their exams all night.
- He was driving home when the accident occurred.
- The children were laughing and playing in the garden.
- We were waiting for the bus when it started to rain.
- She was writing an email when her computer crashed.
- They were discussing the project during the meeting.
- I was listening to music while working on my homework.
Affirmative form:
- Subject + was/were + verb (present participle)
Negative form:
- Subject + was/were + not + verb (present participle)
Interrogative form:
- Was/Were + subject + verb (present participle)?
The past progressive is used in the following situations:
- Interrupted actions in the past
- Specific time frame as an interruption
- Simultaneous actions
- Setting the scene
- Repeated or irritation actions
