
In the intricate world of language rules and tenses, the future perfect tense stands out as a unique tool for looking ahead, but with a backward glance. It enables us to express actions that will be completed at a specific point in the future. In this way, the future perfect creates a bridge between the present and a future moment. This article will thoroughly explain this tense by providing its structures, examples, and exercises.
Definition: Future perfect
The future perfect tense is a verb tense that refers to actions that will have been completed before or by a certain point in the future. It employs two essential auxiliary verbs, combined with the past participle of the main verb. This tense allows the speaker to project themselves into the future and describe a completed action relative to another future action or retrospective time. This tense essentially conveys the idea that an action is already finished by a future moment, typically used when discussing deadlines, plans, or goals.
Formula of future perfect active voice
The future perfect tense belongs to one of the three perfect tenses – which include the past perfect and the present perfect tenses. Unlike the present or past tenses, there is no subject-verb agreement variation since the auxiliary verb “will” stays the same for all subjects and pronouns, whether singular or plural. The past participle (3rd past form) of the relevant verb, however, depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular. You can learn more about these irregular verbs conjugations in our past simple article. The structure of the active form is outlined in the following:
Structure
Subject + will have + past participle + rest of the sentence.
Examples
Instead of “will,” “shall” can be used in very formal situations. Similar to future simple, this is rarely the case in social contexts, as the use of “shall” is very archaic.
Active question form of future perfect
To form questions in the active future perfect, the auxiliary verb “will” is moved to the beginning of the sentence, followed by the subject, the rest of the formula, and a question mark.
Structure
Will + subject + have + past participle + rest of the sentence?
Examples
Negative question form of future perfect
In the negative question form of future perfect, “not” is inserted after “will,” often in its contracted form as “won’t.” When using question words, you simply add them to the beginning of the sentence.
Structure
Will + subject + not + have + past participle + rest of the sentence?
Or
Won’t + subject + have + past participle + rest of the sentence?
Examples
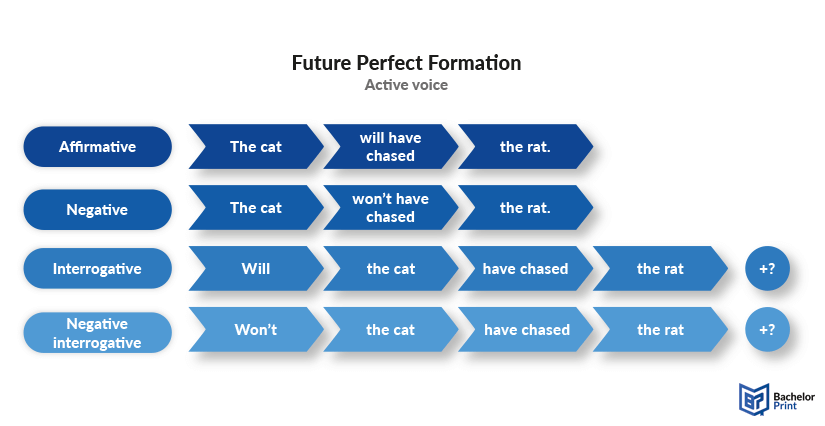
The image below illustrates all active forms of the future perfect tense.
Practice worksheet
Before we explore the passive voice of future perfect, here is a quick test with 10 sentences to practice. Fill in the blanks using the correct future perfect structure. The answers are available in the second tab.
- She ____ her homework by the time you call. (To finish)
- They ____ the building before noon. (To leave)
- By next week, we ____ the new product design. (To complete)
- I ____by the time the meeting starts. (To arrive, negative)
- ____ you ____ your project by the deadline? (To finish, interrogative)
- He ____ the email by the end of the day. (To send)
- We ____ the task by tomorrow. (To complete, negative)
- ____ they ____ for the marathon by next month? (To train, interrogative)
- You ____ the book before the class begins. (To read)
- ____ she ____ dinner by the time I get home? (To cook, interrogative)
- She will have finished her homework by the time you call. (To finish)
- They will have left the building before noon. (To leave)
- By next week, we will have completed the new product design. (To complete)
- I will not have arrived by the time the meeting starts. (To arrive, negative)
- Will you have finished your project by the deadline? (To finish, interrogative)
- He will have sent the email by the end of the day. (To send)
- We won’t have completed the task by tomorrow. (To complete, negative)
- Will they have trained for the marathon by next month? (To train, interrogative)
- You will have read the book before the class begins. (To read)
- Will she have cooked dinner by the time I get home? (To cook, interrogative)
Formula of future perfect passive voice
In the passive voice, the future perfect construction focuses on the action being completed and not on who performed the action. When people are involved, we add the “by” agent right before the object. The passive future perfect formula changes slightly by adding in the auxiliary verb “been” before the main verb. The passive future perfect forms follow the following structures.
Structure
Subject + will have + been + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Examples
Structure
Subject + will not + have been + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Or
Subject + won’t + have been + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Examples
Structure
Will + subject + have been + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Examples
Structure
Will + subject + not have been + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Or
Won’t + subject + have been + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Examples
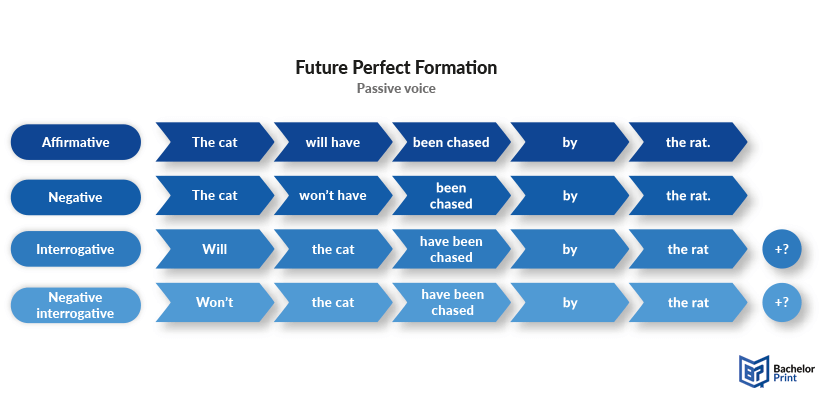
Below, we have created an image portraying all forms in passive voice.
Indicators of the future perfect
Certain time expressions are commonly used with the future perfect to establish a future point by which an action will have been completed. These time markers help specify when the action will be finished.
This indicates that the action will be completed before or by a specific future time of reference.
This time marker indicates the duration in which an action will be completed.
This preposition is used when an action is completed prior to another event.
This indicates an action that will be completed immediately following another action.
“When” is used to indicate a specific future event that triggers the completion of an action.
This preposition emphasizes that something will have been completed earlier than expected.
In the future perfect, it is used to underline a point in the future from the current moment.
However, there is something that should be noted for the second example.
Note: The future construction using the auxiliary verb “to be” can be easily confused with the future perfect continuous tense, so be careful when using it. E.g., “We will have been married” implies a state of being married, which fits the continuous aspect, even though it uses the structure of future perfect.
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
Short answers in future perfect
Short answers are used to respond briefly without reciting the entire sentence.
Active voice
Structure
Positive: Yes, + subject + will have.
Negative: No, subject + won’t have.
Passive voice
Structure
Positive: Yes, + subject + will have been.
Negative: No, subject + won’t have been.
Future perfect vs. future simple
Both future perfect and future simple tenses refer to actions or events that happen in the future, but they differ in how they describe the timing and completion of these events.
Future perfect
The future perfect tense (orange) is used to describe an action that will be completed by a specific point in the future. It emphasizes that the action will have been finished before a certain future time or event.
Future simple
The simple future tense (purple) is used to describe actions that will happen in the future without any specifics. It focuses primarily on decisions, promises, or actions that will take place.
Future perfect vs. future perfect continuous
The future perfect and future perfect continuous tenses are used to describe actions that will be completed or in progress at a specific point in the future. However, their structures and usage differ quite considerably, making them easy to not mix up.
Future perfect continuous
This continuous tense’s emphasis is on the duration or continuation of an action up to a certain point in the future. It illustrates that something will have been in progress by using the present participle of the main verb.
Structure
Subject + will have been + present participle + rest of the sentence.
Examples
Practice exercise
To wrap up everything we have learned, here is a practice exercise to test your understanding of the future perfect tense. Below are ten sentences using active, passive, negative, and interrogative forms of future perfect. Identify and understand how this tense is used in each sentence by filling in the blanks with the voice or form indicated at the end of each sentence.
- The house ____ by the end of next week. (To paint, passive)
- By tomorrow, they ____ all the reports. (To complete, active)
- She ____ the project before the deadline. (To finish, negative)
- ____ the meeting ____ by the time we arrive? (To start, interrogative)
- The presentation ____ by the speaker before lunch. (To deliver, passive)
- ____ they ____ to the new house by the end of the month? (To move, negative)
- We ____ the renovations by next Friday. (To finish, active)
- The contract ____ before the boss returns. (To sign, negative, passive)
- ____ you ____ the article by next Monday? (To write, interrogative)
- The car ____ by the mechanic before the weekend. (To fix, passive)
- The house will have been painted by the end of next week. (To paint, passive)
- By tomorrow, they will have completed all the reports. (To complete, active)
- She won’t have finished the project before the deadline. (To finish, negative)
- Will the meeting have started by the time we arrive? (To start, interrogative)
- The presentation will have been delivered by the speaker before lunch. (To deliver, passive)
- Won’t they have moved to the new house by the end of the month? (To move, negative)
- We will have finished the renovations by next Friday. (To finish, active)
- The contract won’t have been signed before the boss returns. (To sign, negative, passive)
- Will you have written the article by next Monday? (To write, interrogative)
- The car will have been fixed by the mechanic before the weekend. (To fix, passive)
FAQs
The future perfect tense is used to describe an action that will have been completed by a specific time of occurrence in the future. This tense is often used to discuss deadlines, achievements, or any future point where an action will be done.
Examples
- By this time next year, I will have graduated from college.
- She will have finished the project by the time the meeting starts.
- By next month, I will have moved to a new city.
- They will have completed the construction by the end of the year.
- She will have written the report by Friday.
- We will have finished our presentation by the time you arrive.
- The flight will have landed before 6 PM tomorrow.
- He will have learned how to swim by next summer.
- They will have saved enough money for a vacation by the end of the year.
- I will have cleaned the house before the guests arrive.
- By the time you read this, I will have left for the airport.
- The company will have launched the new product by the end of this quarter.
The future perfect tense of “to finish” is “will have finished” for all pronouns.
