
The methodology of academic writing encompasses various types of research, each with its unique approach and purpose. From qualitative to quantitative, experimental to correlational, understanding these different types is crucial to select the right approach for your study. Our guide will elucidate these methods. Good research skills are a must for students, so you need to be familiar with the different types of research you can use.
Definition: Types of research
There are many different types of research based on their purpose, the type of data involved, the sources used, etc.
Which types of research you use depends on your area of study and the scope of your project.
Types of research – Purpose
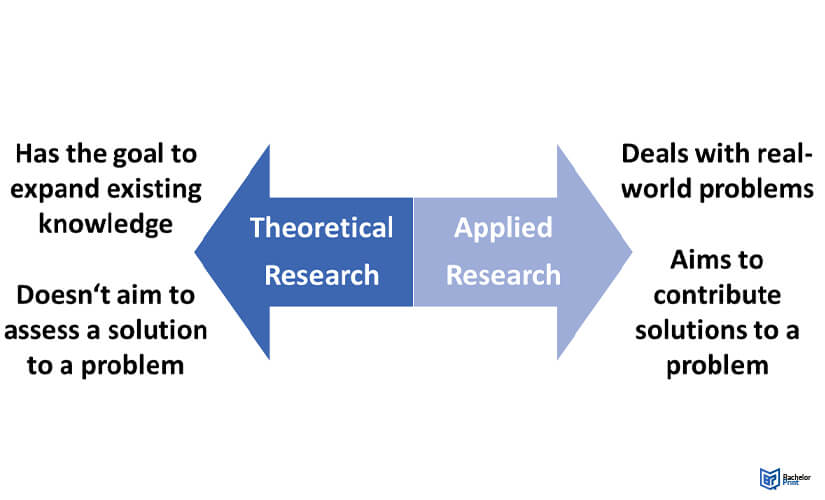
Theoretical Research
This type of research deepens or expands existing knowledge, but it doesn’t try to solve specific problems.
Applied Research
Applied research focuses on real-world issues and its conclusions have practical applications.
Types of research – Depth of scope
Exploratory research
This type of research aims to provide a general framework around a particular topic, without going into too much detail.
Descriptive research
Descriptive research gathers extensive data about a topic or about research subjects, so it has a deeper scope than exploratory research.
Explanatory research
This type of research focuses on answering “why”-questions. This requires a detailed cause-and-effect assessment.
Correlational research
This research compares two facts or data sets, to find meaningful connections between them.
Types of research – Type of data
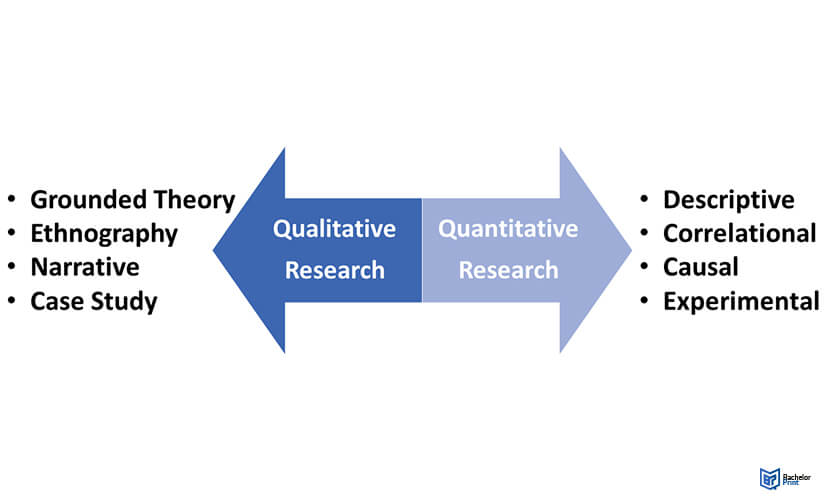
Qualitative research
Data consists of words or concepts, which can be assessed and interpreted but not objectively measured.
Quantitative research
This research relies on any data units that can be objectively measured.
Types of research – Manipulation of variables
Experimental Research
Independent variables are applied to dependent variables to determine their impact and to test a hypothesis.
Non-Experimental research
Non-experimental research doesn’t manipulate the independent variable, and it’s not always necessary to find a correlation between variables.
Quasi-experimental research
This is similar to experimental research, but the main difference is that in quasi-experimental research, research subjects aren’t randomly assigned to different groups.
Types of research – Type of inference
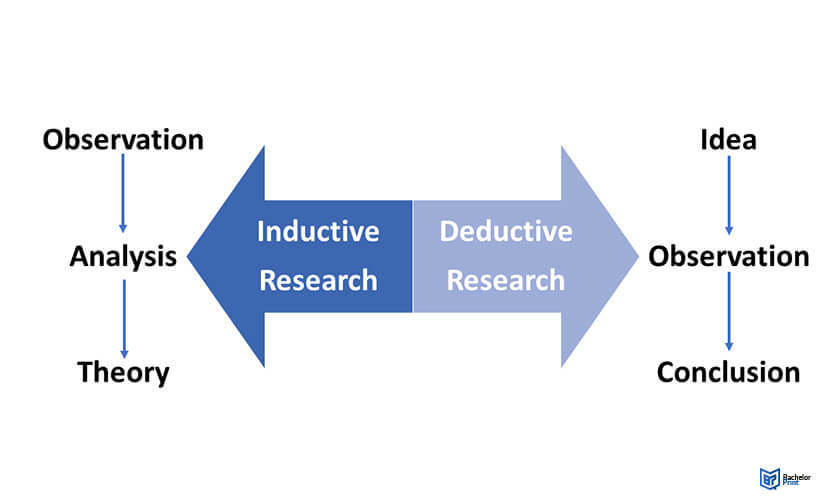
Deductive research
In deductive research, inferences or conclusions are reached by testing a theory and/or a hypothesis. Data is collected and analyzed to either prove or disprove the hypothesis.
Inductive research
The starting point isn’t a theory or hypothesis, but a set of observations that can later be turned into generalizations.
Types of research – Time of execution
Diachronic research
Diachronic research studies a fact or phenomenon over a period of time.
Synchronous research
Synchronous research examines a fact or phenomenon as it happens during a specific point in time.
Types of research – Sources of information
Primary research
This means that your data comes from your own research.
Secondary research
This means that your research data comes from existing sources.
Types of research – State of data
Documentary
Data consists of existing official documents, photos, personal communications, or audio files.
Field
Field data is created and collected in real-world settings, for example in the form of interviews, surveys, etc.
Laboratory
Lab data is usually collected in lab settings under controlled conditions.
Mixed-Method: Documentary, field, and/or laboratory
This refers to the combination of all three types of research in a single study.
FAQs
In terms of purpose, the 2 main types of research are theoretical and applied. In terms of the data used, research can be classified into qualitative and quantitative.
Yes, using several types of research is possible as long as they’re compatible and suited to your topic and research question.
A research question, data, and a framework to analyze the data.
Not always. This is more common if you’re doing quantitative research.
