
An observational study, a key component of research methodology, permits researchers to draw inferences from a target sample through unobtrusive observations. In this approach, variables or conditions remain unaltered while researchers record only those characteristics that are directly observable. This strategy allows the study to reflect a more naturalistic picture of the target sample, thus preserving ecological validity.
Definition: Observational study
An observational study refers to a research methodology where researchers only consider the observable variables in a study. No attempt is made to control or set any conditions to influence the study’s findings.
The types of observation used in an observational study
There are several types of observation in observational studies. They can be classified as follows:
| Type | Description | Example |
| Naturalistic observation | It entails studying objects in their natural environment without interference | Observing animals in a game park |
| Participant observation | The researcher is part of the day-to-day life of the research participants | Living in a community with the participants |
| Systematic observation | It’s a precise list of actions and methodology to be used in studying specific variables | A patient’s behaviour can be monitored using tests, interviews, tasks, and other tools |
| Covert observation | The participants don’t know they are being observed | Observing and interacting with shoppers at a mall |
| Quantitative observation | Uses statistical and numerical tools and methods to measure quantifiable variables | Calculating the average income of people in their 30s in a city |
| Qualitative observation | Data is collected through the 5 senses – sight, smell, taste, hearing, and touch | Observing the taste of food, the texture of a fabric |
| Case study | It is an intensive focus on a single group or unit | Observing students in their final semester in school |
| Archival research | It involves using information from original archives and repositories | Reviewing government birth records |
Observational study types
Observational studies are used in different research contexts. Researchers can observe different characteristics using the following types of observational studies:



This type of study uses two groups. One group has an additional variable that is absent from the other. Researchers carry out case-control observations to measure the effect of the variable on an outcome.
Cohort studies track participants over time. They are primarily used to observe a population with common characteristics. For instance, cohort studies can be used in studying people in a given occupation or the inhabitants of a place.
It focuses on a set of variables at a specific time. Researchers use cross-sectional analysis to analyse themes that occur in a single instance.
An Observational Study Step by Step
The scope of an observational study spans the elements of data collection and selecting the right population. You can use the following steps:
Step 1: Establish the research question and goals
Defining your research problem entails identifying the methods of observation to be used. It may involve the following:
- Why are you interested in observing a group?
- What is the scope of your observation?
- What ethical concerns may affect your study?
Step 2: Determine the observation type and technique
You may consider the following in choosing your technique:
- Do you have a pre-selected observation, or will you formulate it as you go along?
- Can you use another research method in your observational study?
- What is the effect of doing a covert observation versus notifying the participants?
- How can you prevent confounding variables that may affect your analysis?
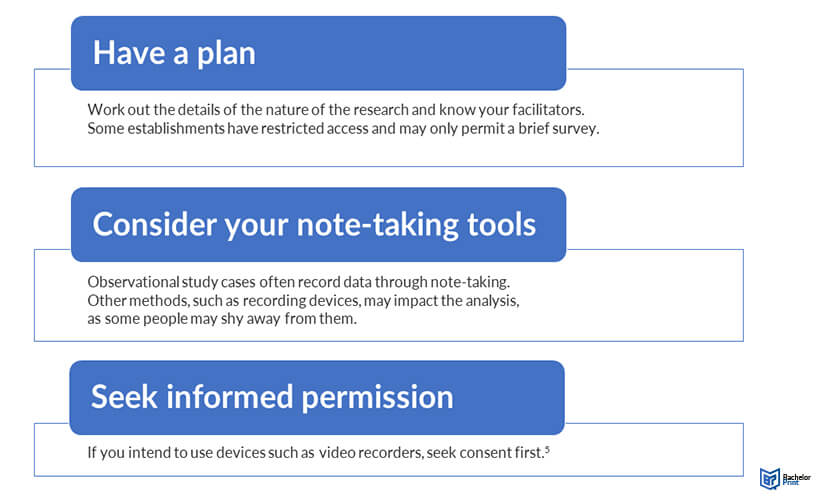
Step 3: Set up and conduct the observational study
Here are a few pointers before you begin your observational study:
Step 4: analysing the results
The methods used to analyse, depend on the nature of the observational study.
You could use an inductive approach if your observation was done in an open-ended manner.
A deductive approach is more suitable when there are established hypotheses before the study.
An in-depth example of an observational study
You may want to study the customer habits of a brand. You can observe the following variables:
- How much time customers spend at a store.
- Online ratings of the store.
- Ages of the people who shop there.
You can decide on one characteristic that you want to study. For example, how much time do buying customers spend at the store? With this research question, you can choose the cohort observation type as your population has a common characteristic. You can check the ratings to identify what customers like and dislike. You may also engage the staff of the store in the study.
Advantages and disadvantages of an observational study
Observational studies are used because they have several benefits. However, like other research methods, they have some drawbacks.
| ✓ Advantages | ✗ Disadvantages |
| It is one of the easiest methods of study. | It is impossible to observe everything. A researcher can only observe and record a few things simultaneously, and other variables may go unnoticed. |
| It is carried out in natural surroundings where no variables are influenced, making it a reliable method. | It can be time-consuming since the methodology uses simple tools that cannot accumulate a lot of data in a short time. |
| It is the most appropriate method for specific subjects. | It does not take into account past events. An observational study is tied to the present, and past factors are not accounted for. |
| It offers accurate data as the researcher is present in the research environment. | The risk of bias. The results of the observational study are subject to the view and interpretation of the researcher. Some thoughts may be influenced by personal biases. |
| It can easily be coordinated with minimal effort or resources. |
FAQs
Observing workers in a factory. The subjects are observed in their natural state as they work and interact with their colleagues. A covert approach may be used where the observations are made without the workers’ knowledge.
We use observational methods where the variable under investigation can be observed and recorded in real time. Researchers also employ observation techniques in cases where other research methods are unusable.
A cohort observation is a research method where a group with a similar trait is studied. Researchers may use such a sample to study phenomena unique to such groups.
A control group is a group of people exempted from a research condition. They are used to test the effect of the condition on another group in observational research.
