
When conducting a study, you often find yourself confronted with an accumulation of data, which needs to be interpreted. Central tendency, a key concept within the realm of statistics, aids in understanding the central or typical value in a dataset. The different measures form the backbone of many statistical analyses, providing insight into the distribution of data points. In our subsequent discussions, we will delve into how these vital measures of central tendency are employed to synthesize the results of a study.
Definition: Central tendency
Central tendency is an umbrella term for measures describing a dataset with a single value that represents the middle of the distribution. These include:
- The mode – the most frequent value in the set.
- The median – the middle value of the set.
- The mean – the average of the set.
Even though it does not measure central tendency, some people count the range of data also as one of them. This measurement simply defines the difference between the highest and lowest value in the dataset.
Mode
The mode is the most frequent value in the dataset, which you can easily find by counting how often which value exists in the set. Depending on your sample, you can get one mode, multiple or none at all. If you visualize your data in a graph determined by frequency, the highest bar or point on the curve is your mode.
Median
The median is the middle value in a dataset arranged in ascending or descending order, dividing the distribution in half. To calculate the median in a set that is too big to simply count, you divide the number of values by two. If it is an odd numbered set, you will get an x.5 number, which you have to adjust upwards (e.g., set with 125 values → 125/2= 62.5 → Mode= value on position 63). If the set is even numbered, you will add the two middle numbers together and divide the result by two (e.g., set with 126 values → 126/2=63 → Mode=63+64/2=63.5).
Mean
There are two different types of mean, the arithmetic and the geometric mean, which both calculate the average of a dataset.
Arithmetic mean
The arithmetic mean divides the sum of values by the number of values. It describes the average of a dataset and is mostly used with discrete, integral data.
Geometric mean
The geometric mean multiplies all values and then extracts the nth root, with n being the number of values. It also describes the average of a dataset, but is mostly used with continuous, fractioned data or wide ranges.
Range of data
The range of data in a set is technically not a measure of central tendency, but it is still sometimes counted in with them. The range just subtracts the lowest value from the highest value to determine how far the set is reached on both sides.
Outlier effect
An outlier is an extreme value that does not quite fit in with the rest. It can be either high above the others or much below. Outliers can have different effects on datasets, like skewing the distribution, and also on measures of central tendency.
The mode is generally little affected by outliers, as the most frequent value is often very clear. In cases like this, outliers only become interesting if they are the mode or very close. For example, if your dataset consists of numerical answers like 1,2,3,4,5 and 31 and 2 as well as 31 are the most frequent values. However, the interpretation of an outcome like this is very individual and depends on the study and situation.
The median is never affected by outliers, as only the number of values is important and not their actual value. Both types of mean are certainly affected by outliers, since each value is included into the calculation
Distributions
In different distributions, you will find the measures of central tendency in different places.
Normal distribution
A normal distribution is symmetrical and has its highest point in the middle of the curve. Thus, the mode, the median, and the mean are all the same.
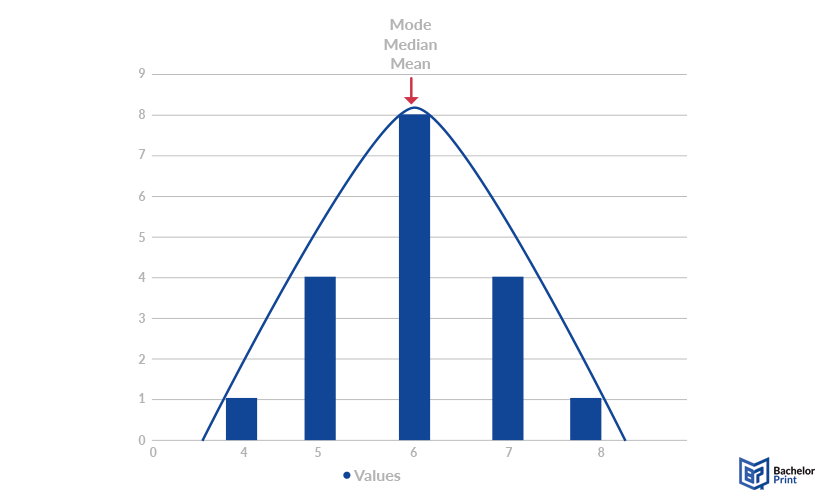
Skewed distributions
No matter whether the distribution is positively skewed (highest point closer to the y-axis) or negatively skewed (highest point further away from the x-axis), the mode can always be found at the highest point, the mean, and median follow downwards towards the longer end. In this case, however, the median and mean have to be calculated and can most likely not be drawn from the graph.
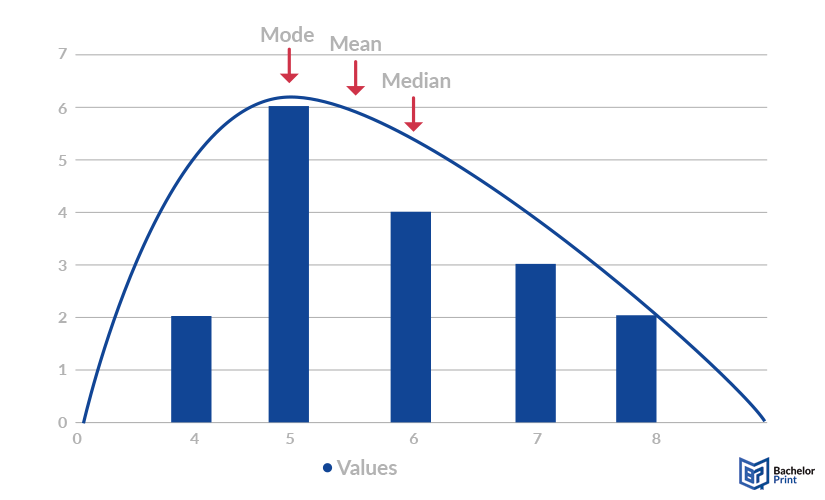
When to use which
Knowing when to apply which measure of central tendency is important in statistics, since they give valuable insight on your data.
As a short overview of the different types of variables, categorical variables are divided into nominal data, which includes individual values that cannot be ranked, and ordinal data, which is qualitative data that can be ranked. Furthermore, you can divide quantitative data into discrete, meaning countable data, and continuous, meaning that there are infinite values on a line, such as time or length.
The following table will explain when each measure of central tendency can be used and why or why not.
Mode
Median
Arithmetic mean
Geometric mean
Nominal v.
x
Ordinal v.
x
Only odd numbered
Only if numbered
Discrete v.
x
x
x
x
Continuous v.
Only in intervals
x
x
x
The mode can be used with every type of data, since even if you only have a nominal variable, there will most likely be one value chosen more often than the other. When there are multiple possible values, the outcome will most likely be multimodal, but this depends on the individual topic. If, however, there are too many values in the dataset, the mode is not as expressive.
Continuous variables are generally not suited for defining a mode due to the fact that they are measured instead of counted. Thus, it is nearly impossible to gain the exact same value twice. Only if you divide them into intervals, you can determine a mode-interval, in which most of the values lie.
It is also worth noting the cases where you should never use this method.
- You shouldn’t use this measure if all values appear the same number of times.
- Also, it shouldn’t be used if there is a very small number of values.
Determining the median is not possible for nominal data, since it cannot be ranked or brought in a useful order. Furthermore, as the median is actually calculated, it is also not possible for even-numbered ordinal data, as you cannot perform mathematical operations with qualitative data. However, if the ordinal dataset is odd-numbered, it is possible, since the middle value can simply be counted.
For discrete and continuous data, the median can always be calculated, as the values are numerical and can be used in the mathematical operations needed to determine this measure of central tendency.
With nominal variables, you can never calculate the arithmetic mean, as there is no “average” between qualitative categories. The same applies to ordinal variables in general. However, if you number the ranks, you can theoretically calculate the arithmetic mean, but this is not common practice in statistics.
With discrete as well as continuous data, the arithmetic average is a widely used measurement and can be calculated with no problems.
The geometric mean can only be applied with quantitative data, meaning discrete and continuous variables, as these are the only types where mathematical operations can be performed.
In theory, calculating the geometric mean with numbered ordinal data would be possible. However, it is never used in such cases, since the arithmetic mean would be the preferred measure of mean.
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
FAQs
The measures of central tendency include the mean, mode, and median.
If the distribution is strongly skewed, you should use the median because it is least affected by outliers due to the fact that is considers the number of values, not the values themselves.
You can use mode on all levels of data, but median and mean cannot be used on nominal data and in some cases not even with ordinal data.
Outliers have no effect on the median and very little on the mode, since they consider mostly the number of values rather than the values themselves. The mean, however, is highly affected by outliers, as every value influences the result of the calculation.
