The future continuous tense is one of the essential tenses in English that falls under the broader category of language rules. It serves a specific purpose by expressing actions or events that will be happening. Under- standing this tense is key to mastering fluent and natural communication. In this article, we will explain the future continuous thoroughly, along with its structures and examples.
Definition: Future continuous
The future continuous is a verb tense used to express actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future. It conveys a sense of duration, indicating that something will be happening at a certain point. Future continuous can often imply a future plan or expectation, allowing speakers to describe an activity that will already be happening when something else occurs. Auxiliary verbs (or helper verbs) and participles aid its structure, allowing the main verb to convey ongoing or completed actions across different time frames.
Formula of future continuous active voice
The structure of future continuous (or future progressive) is the future version of the present continuous, and follows a specific formula that ensures subject-verb agreement, as it uses the same auxiliary verbs (“will” and “be”) for all singular and plural pronouns or subjects. The verb remains in the present participle form (the “-ing” form), making the structure of the future continuous easy to understand.
Structure
Subject + will be + present participle + rest of the sentence.
Examples
Similarly to future simple, contractions can be used in the future continuous form. Turning “she will be” into “she’ll be,” while the negative form “she will not be” turns into “she won’t be.”
Note: To create a similar meaning, “be going to” can be used instead of “will.” E.g., “You will be waiting” turns into “You are going to be waiting.” Both forms are usually interchangeable, unlike simple future forms.
Active question form of future continuous
For the future continuous question form, we adjust the sentence structure by placing “will” at the beginning of the sentence. The auxiliary verb “be” remains behind the subject, followed by the main verb.
Structure
Will + subject + be + present participle + rest of the sentence?
Examples
Questions with question words
When asking future continuous questions using question words, the word order remains the same, but the question word is placed at the front.
Negative question form of future continuous
The negative interrogative sentence form in the future continuous tense adds “not” after “will” and the subject to express doubt or seek confirmation. As previously mentioned, a contraction can also be used in the negative question form of future continuous.
Structure
Will + subject + not + be + present participle + rest of the sentence?
Or
Won’t + subject + be + present participle + rest of the sentence?
Examples
Negative questions with question words
When forming negative questions with question word in future continuous, the question word is added to the start of it.
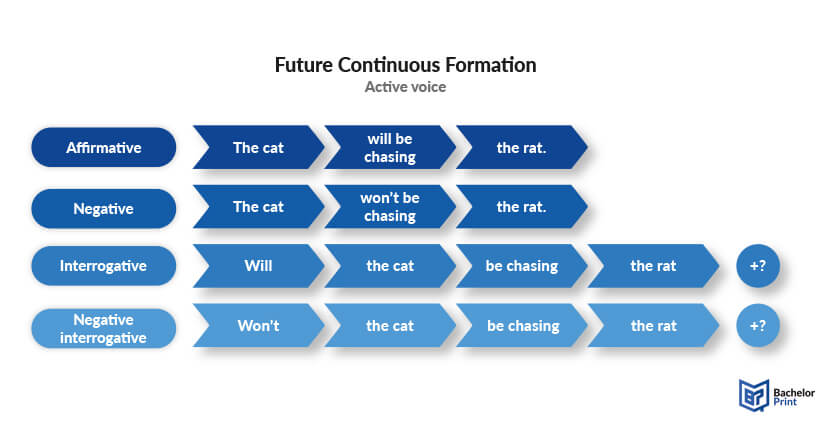
The image below illustrates all structures of the future continuous active voice.
Practice worksheet
The practice sentences cover all aspects of the future continuous mentioned in the previous paragraphs. The second tab contains the correct verb conjugations in the future continuous.
- At 8 PM tomorrow, I ________ (study) for my exams.
- They ________ (not attend) the concert because of the weather.
- ________ (you, work) on the presentation all day tomorrow?
- What ________ (she, wear) to the party?
- We ________ (wait) for you at the train station at 5 PM.
- Where ________ (he, live) during his stay in Paris?
- ________ (they, play) football this evening?
- Why ________ (you, not participate) in the competition?
- By this time next week, she ________ (relax) on a beach.
- Will he ________ (run) the marathon tomorrow morning?
- At 8 PM tomorrow, I will be studying for my exams.
- They will not be attending the concert because of the weather.
- Will you be working on the presentation all day tomorrow?
- What will she be wearing to the party?
- We will be waiting for you at the train station at 5 PM.
- Where will he be living during his stay in Paris?
- Will they be playing football this evening?
- Why won’t you be participating in the competition?
- By this time next week, she will be relaxing on a beach.
- Will he be running the marathon tomorrow morning?
Formula of future continuous passive voice
The future continuous tense in passive voice is formed by using “will be,” the present participle “being,” and the past participle (3rd past form) of the verb. After the verb, the “by” agent indicates the doer of the action, and turns the subject of an active sentence into the object of a passive sentence and vice versa.
Structure
Subject + will be + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Examples
Structure
Subject + will not + be + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Or
Subject + won’t be + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Examples
Structure
Will + subject + be + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Examples
Structure
Will + subject + not be + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Or
Won’t + subject + be + being + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Examples
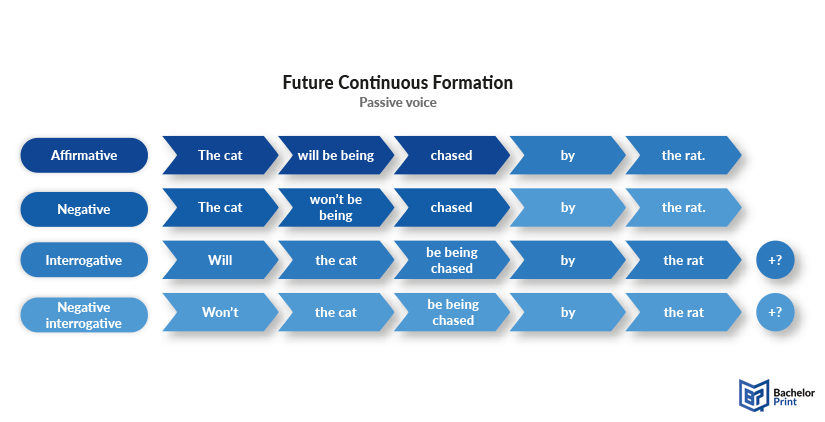
Below, we created an image illustrating all forms of the future continuous in passive voice.
Indicators and usage of future continuous
The future continuous tense can be used in several situations. In this section, we will elaborate on its usage and main indicators, along with numerous examples.
The future continuous tense can describe an action that will be interrupted by another action in the future, meaning that the ongoing action is in progress when the interruption occurs.
This usage focuses on the fact that an action will be happening at a precise future time, and something might interrupt or simply coincide with that exact time.
The future continuous is used to describe two or more actions that will be happening at the same time. This helps to paint a picture of multiple things happening in parallel.
Even though all future events are hypothetical, future continuous is specifically used for hypothetical events that are likely to happen or that you wish to portray as likely (such as predictions).
The future progressive tense can create an atmosphere by describing the ongoing actions surrounding future situations. It gives a sense of the environment and what people will be doing in the background.
Time expressions
The future continuous tense often uses specific time expressions to clarify when the action will be happening. Some common expressions include:
- At this time next week/month etc.
- Tomorrow/Tonight at (specific time)
- In the evening/afternoon etc.
- Soon/Later
- ✓ 3D live preview of your individual configuration
- ✓ Free express delivery for every single purchase
- ✓ Top-notch bindings with customised embossing

Short answers in future continuous
Short answers are used to answer yes/no questions quickly without repeating the whole sentence. The phrasing of the brief responses reveals the subject and whether the response is positive or negative.
Active voice
Structure
Affirmative: Yes, + subject + will be.
Negative: No, subject + will not/won’t be.
Passive voice
Structure
Affirmative: Yes, + subject + will be.
Negative: No, subject + will not/won’t be.
Future continuous vs. future simple
Both future continuous and simple future tenses refer to actions that take place in the future, yet they serve two distinct purposes.
Future continuous
It is typically used for ongoing actions with a specified time frame and gives a sense of duration. This tense (in purple) also shows more certainty that something will be happening.
Future simple
This tense (in orange) refers to actions that will happen at some point without emphasis on their continuity or duration. The certainty of this event or action happening correspondingly seems less likely.
Practice exercise
As a final test, fill in the gaps by using the correct form we have learnt in this article. This will include active, passive, negative, and interrogative forms.
- I ____ my friends at the café tomorrow evening. (To meet, active)
- She ____ the conference next week. (To attend, negative)
- ____ they ____ on the project when I arrive? (To work, interrogative)
- ____ you ____ to the party later? (To come, negative interrogative)
- The new policies ____ by the company. (To implement, passive)
- The building ____ by the authorities. (To inspect, passive, negative)
- ____ the proposal ____ by the board tomorrow? (To review, passive, interrogative)
- ____ the documents ____ by the team? (To prepare, passive, interrogative)
- By this time tomorrow, ____ to the airport. (To drive, active)
- ____ the contract ____ by the client this afternoon? (To sign, passive, interrogative)
- I will be meeting my friends at the café tomorrow evening. (To meet, active)
- She will not be attending the conference next week. (To attend, negative)
- Will they be working on the project when I arrive? (To work, interrogative)
- Will you not be coming to the party later? (To come, negative interrogative)
- The new policies will be being implemented by the company. (To implement, passive)
- The building will not be being inspected by the authorities. (To inspect, passive, negative)
- Will the proposal be being reviewed by the board tomorrow? (To review, passive, interrogative)
- Will the documents not be being prepared by the team? (To prepare, passive, interrogative)
- By this time tomorrow, we will be driving to the airport. (To drive, active)
- Will the contract be being signed by the client this afternoon? (To sign, passive, interrogative)
FAQs
- I will be meeting my friends at the café tomorrow evening.
- She will not be attending the conference next week.
- Will they be working on the project when I arrive?
- Will you not be coming to the party later?
- The new policies will be being implemented by the company next month.
- The building will not be being inspected by the authorities tomorrow.
- Will the proposal be being reviewed by the board next Monday?
- Will the documents not be being prepared by the legal team?
- By this time tomorrow, we will be driving to the airport.
- Will the contract be being signed by the client this afternoon?
You can use the future continuous tense in the following situations:
1. Interrupted actions in the future
- I will be studying when you arrive.
2. Specific time in the future
- At 10 PM tomorrow, I will be watching a film.
3. Simultaneous actions in the future
- She will be cooking dinner while I am working.
4. Ambience of a situation
- During the concert, people will be singing and dancing.
The difference between future progressive and simple future tenses are as follows:
- Future continuous describes an action that will be ongoing at a specific full stop of time in the future, emphasizing its duration or progress.
Example: At 8 PM tonight, I will be watching (In progress at a specific future time.)
- Future simple describes a simple future action or event, often used for decisions made currently, promises, predictions, or scheduled events.
Example: I will watch TV tonight. (No focus on the duration or progress.)
The rule for forming the future continuous tense uses the auxiliary verb “be,” and is structured as follows:
Structure: Subject + will + be + present participle of the verb.