
Completing a research or thesis paper is more work than most students imagine. For instance, you must conduct experiments before coming up with conclusions. Random assignment, a key methodology in academic research, ensures every participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group within an experiment. In experimental studies, the random assignment of participants is a vital element, which this article will discuss.
Definition: Random assignment
Pearson Correlation is a descriptive statistical procedure that describes the measure of linear dependence between two variables. It entails a sample, control group, experimental design, and randomized design. In this statistical procedure, random assignment is used. Random assignment is the random placement of participants into different groups in experimental research.
Importance of random assignment
Random assessment is essential for strengthening the internal validity of experimental research. Internal validity helps make a casual relationship’s conclusions reliable and trustworthy.
In experimental research, researchers isolate independent variables and manipulate them as they assess the impact while managing other variables. To achieve this, an independent variable for diverse member groups is vital. This experimental design is called an independent or between-group design.
This assignment technique in experiments ensures no bias in the treatment sets at the beginning of the trials. Therefore, if you do not use this technique, you won’t be able to exclude any alternate clarifications for your findings.
Even with random participant assignment, other extraneous variables may still create bias in experiment results. However, these variations are usually low, hence should not hinder your research. Therefore, using random placement in experiments is highly necessary, especially where it is ethically required or makes sense for your research subject.
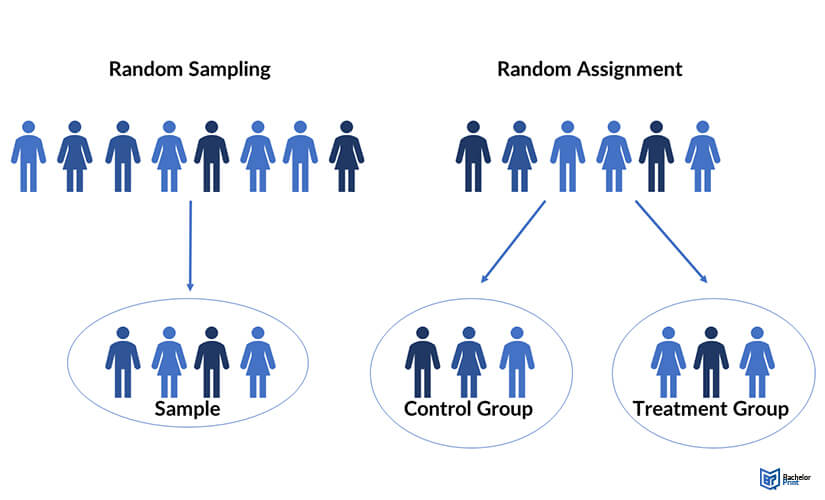
Random assignment vs. random sampling
Simple random sampling is a method of choosing the participants for a study. On the other hand, the random assignment involves sorting the participants selected through random sampling. Another difference between random sampling and random assignment is that the former is used in several types of studies, while the latter is only applied in between-subject experimental designs.
Random sampling enhances external validity, as it guarantees that the study sample is unbiased, and that an entire population is represented. This way, you can conclude that the results of your studies can be accredited to the autonomous variable.
How to use random assignment
Firstly, give each participant a unique number as an identifier. Then, use a specific tool to simplify assigning the participants to the sample groups. Some tools you can use are:
| Tools | Application |
| Random number generators: | Computer programmes to generate numbers from the list of participants |
| Lottery technique: | Place the numbers in a container and draw them randomly for each group |
| Coin toss: | If you have two sets or groups only, you can toss a coin to determine which one will be the regulated or trial group |
| Roll a dice: | If you have three groups, you can roll a dice to determine which participant joins each group. |
Random member assignment is a prevailing technique for placing participants in specific groups because each person has a fair opportunity of being put in either group.
Random assignment in block experimental designs
In complex experimental designs, you must group your participants into blocks before using the random assignment technique.
Depending on their unique characteristics, you can also use blocking in experimental matched designs before matching the participants in each block. Then, you can randomly allot each partaker to one of the treatments in the research and examine the results.
When random assignment is not used
As powerful a tool as it is, random assignment does not apply in all situations. Like the following:
Comparing different groups
When the purpose of your study is to assess the differences between the participants, random member assignment may not work.
No ethical justifiability
Another situation where you cannot use random assignment is if it is ethically not permitted.
FAQs
It is an experimental research technique that involves randomly placing participants from your samples into different groups. It ensures that every sample member has the same opportunity of being in whichever group (control or experimental group).
You can use this placement technique in experiments featuring an independent measures design. It helps ensure that all your sample groups are comparable.
It can help you enhance your study’s validity. This technique also helps ensure that every sample has an equal opportunity of being assigned to a control or trial group.
You should not use this technique if your study focuses on group comparisons or if it is not legally ethical.
